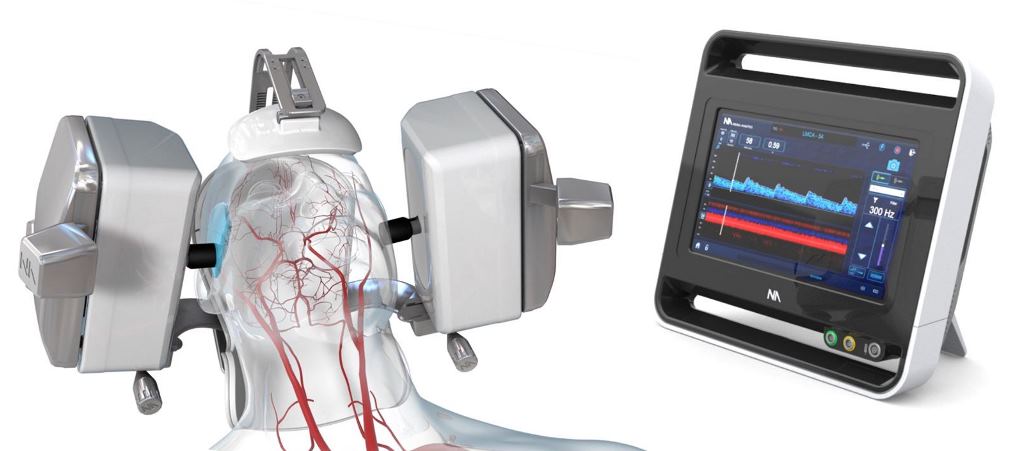
The study, which is being carried out at the Ochsner Clinical Foundation in New Orleans, Louisiana, uses an investigational iteration of the Lucid Robotic System (Lucid M1 Transcranial doppler ultrasound system and NeuralBot system.
The Lucid robotic system is a medical ultrasound device intended for use as an adjunct to standard clinical practices to measure and display CBFV and the occurrence of transient emboli within the brain.
Neural Analytics said the device is not intended to replace other means of assessing vital patient physiological processes.
The company is actively enrolling patients into the research feasibility study with plans to activate up to 15 sites, both domestically and globally.
The primary objective of the CODEX Study is to employ an investigational iteration of the Lucid system, which is a CE Marked and FDA cleared device, to gather and further explore the technical feasibility of the novel technology in a wider range of patients and neurological pathologies where the monitoring of cerebral blood flow velocities (CBFV) would be of benefit.
Neural Analytics is undertaking the study with Ifeanyi Iwuchukwu, assistant professor of Neurocritical Care and Stroke at The Ochsner Clinical Foundation.
Neural Analytics co-founder and chief science officer Robert Hamilton said: “We are pleased and privileged that we are able to partner with Dr. Iwuchukwu and the Ochsner Clinical Foundation in the enrollment of our first patients into the CODEX Study.
“This is a big milestone for us, as we are committed to advancing brain healthcare through transformative technology that empowers clinicians with the critical information needed to make clinical decisions and improve patient outcomes.”
Every year, neurological diseases are claimed to cost the US healthcare system nearly $800bn. Traumatic brain injury, migraine, Alzheimer’s and stroke account for more than $438bn out of the total cost.
Stroke affects more than 795,000 people in the US. It is estimated that someone has a stroke every 40 seconds and someone dies from stroke every 4 minutes. It is a time sensitive disease and requires intervention within 24 hours of onset of symptoms.






