With Pfizer’s Covid-19 vaccine candidate emerging as the leading contender to be used in finally immunising people against the virus, there will inevitably be increased focus on the world’s biggest needle and syringe manufacturers, and the role they will play in making sure it’s administered to millions, if not billions, of people.
Earlier this year, Ireland-based market research and data firm Research and Markets released its forecast for the global syringe and needle market – which it anticipates will grow by a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 10% to 2025.
In its industry assessment, Research and Markets also highlighted some of the major players manufacturing these pieces of equipment in 2020.
We take a closer look at the global companies that could be central to Pfizer’s coronavirus vaccine being administered safely, effectively, and on an unprecedented scale, to patients.
Biggest syringe and needle manufacturers in the world
Becton Dickinson (BD)
US medical technology giant BD is currently leading the global syringe and needle market, according to Research and Markets’ report.
With total sales of more than $17bn across its entire portfolio in 2020, and 65,000 employees working throughout 50 countries, the New Jersey-based company is also one of the biggest names in the broader healthcare industry.
In October 2019, BD launched its Intevia 1ml product – a two-step, disposable auto-injector that combines a prefilled syringe and an auto-injector in one integrated system.
As well as making a range of other injection devices for anaesthesia, insulin administration and fluid transfer, the US firm also works in diagnostics, minimally-invasive surgery and oncology.
The UK government ordered 65 million injection devices from BD in July 2020 in preparation for an effective Covid-19 vaccine becoming available.
B. Braun Melsungen
B. Braun Melsungen is currently the largest Europe-based manufacturer of needle and syringe products in the world – as well as being one of the biggest European medical device firms generally.
The company, which is based in the town of Melsungen in central Germany, generated sales in excess of €7.4bn ($8.75bn) in 2019, and employs close to 65,000 people globally.
It works in a wide range of areas within the healthcare sector, manufacturing medical applications that are used in various types of surgery, sterilisation, orthopaedics and wound care.
B. Braun’s portfolio of needle and syringe products includes its Sterican hypodermic needles – which are deployed in blood sampling, injecting insulin and neural therapy – as well as fine dosage, irrigation and infusion pump syringes.
Terumo
Tokyo-based medical device firm Terumo is currently the largest manufacturer of needles and syringes in the Asia-Pacific region.
It employs more than 25,000 people worldwide, provides medical products in about 160 countries and regions, and – in its most recent financial report – anticipated an annual revenue of ¥600bn ($5.7bn).
Alongside its range of veterinary products, Terumo makes hypodermics – including needles and syringes – infusion and blood collection devices, and intravenous catheters.
The Japanese company also enhanced its portfolio of coronary interventional products in June 2019, partnering with Orchestra BioMed and securing global rights to the US biotech firm’s Virtue sirolimus-eluting balloon (SEB), which is used to treat in-stent restenosis.
Teleflex
Teleflex is an American firm that predominantly focuses on medical devices used in critical care and surgery.
However, it also produces a number of ‘vascular access accessories’ via its Arrow brand – which includes introducer needles, and its Raulerson spring-wire syringes.
The Pennsylvania-based company reported annual sales of close to $2.6bn in 2019, and employs more than 14,000 people in total.
Teleflex acquired fellow US medical device firm and haemorrhage control specialist Z-Medica earlier this year, in October, in a deal worth an estimated $500m, and strengthened its position in areas like hospitals, EMS (emergency medical services) and military call points in the process.
Nipro
Japanese medical equipment manufacturer Nipro works in a variety of healthcare-related areas, including diabetes and renal care, hospital supplies, home infusion therapy, in vitro diagnostics, and pharmaceutical packaging.
In infusion specifically, Nipro makes a range of syringes – which it claims are all designed to be accurate and easy to use – and hypodermic needles, which are “ultra-sharp” to minimise patient discomfort during injection.

According to its website, the Osaka-based firm produces more than 11 billion needle units each year, confirming its place as one of the world’s leading manufacturers in this space.
In March 2020, it also reported annual revenues of about ¥442.5bn ($4.2bn) and the company is believed to have more than 30,000 employees worldwide.
Smiths Medical
Minnesota-based Smiths Medical is a subsidiary of UK medical technology giant Smiths Group, and operates across critical care, cardiology, oncology, anaesthesia, respiratory applications and pain management.
The company posted an annual revenue of almost $1.15bn for 2019, and employs 7,770 people in more than 30 countries – with manufacturing concentrated in the US, UK, Mexico, Italy, Germany, Czech Republic, and China.
As well as making its own needle devices and intravenous catheters, Smiths Medical manufactures several products designed to increase the safety of these medical ‘sharps’, and reduce needlestick injuries.
In July 2020, the firm also announced it had partnered with the US government in the battle against Covid-19 – securing a $20m investment from BARDA (Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority) to increase syringe and needle production as part of the Operation Warp Speed vaccine programme.
Cardinal Health
US- and Ireland-headquartered healthcare heavyweight Cardinal Health is one of the biggest American companies in the world right now, ranking 16th in this year’s Fortune 500 ahead of the likes of General Motors, Microsoft and Johnson & Johnson.
It reported annual revenues of $152.9bn for 2020, and employs close to 50,000 people in more than 45 countries.

The medical products Cardinal Health manufactures range from patient monitoring tools and surgical equipment to PPE (personal protective equipment) and wound management – and the company’s portfolio also includes its Monoject line of needles and syringes.
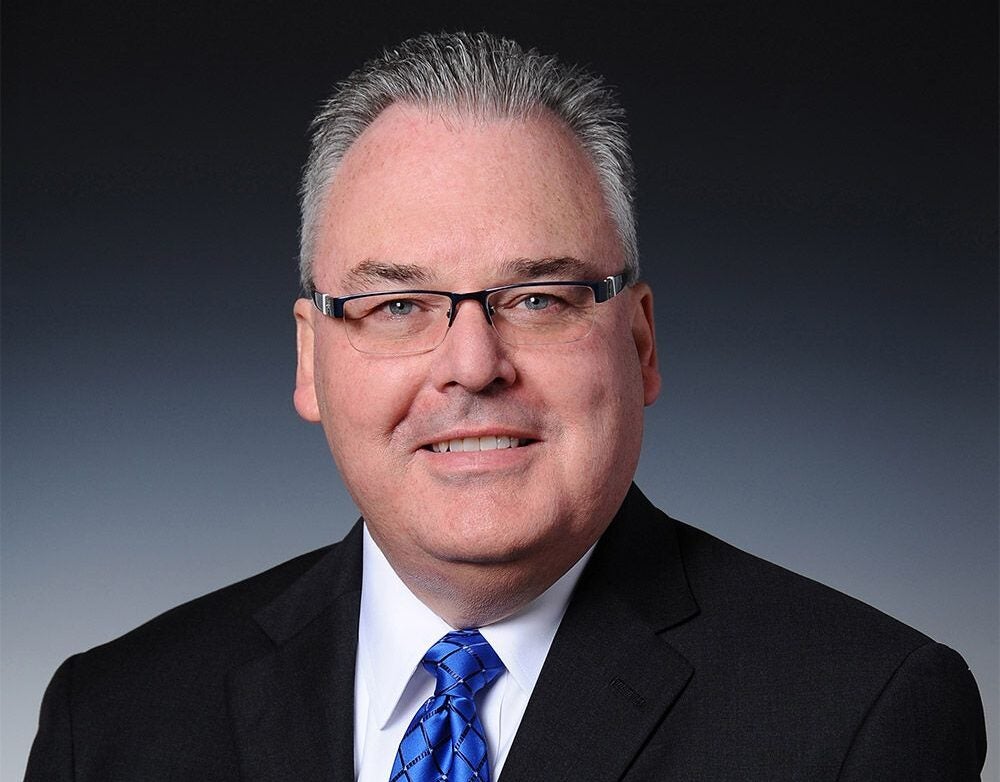
Cardinal Health CEO Mike Kaufmann has been with the firm for 27 years, having previously worked at US accounting giant Arthur Andersen.






