
Entrepix Medical has introduced a new “life-changing” surgical blade technology designed to improve patient healing.
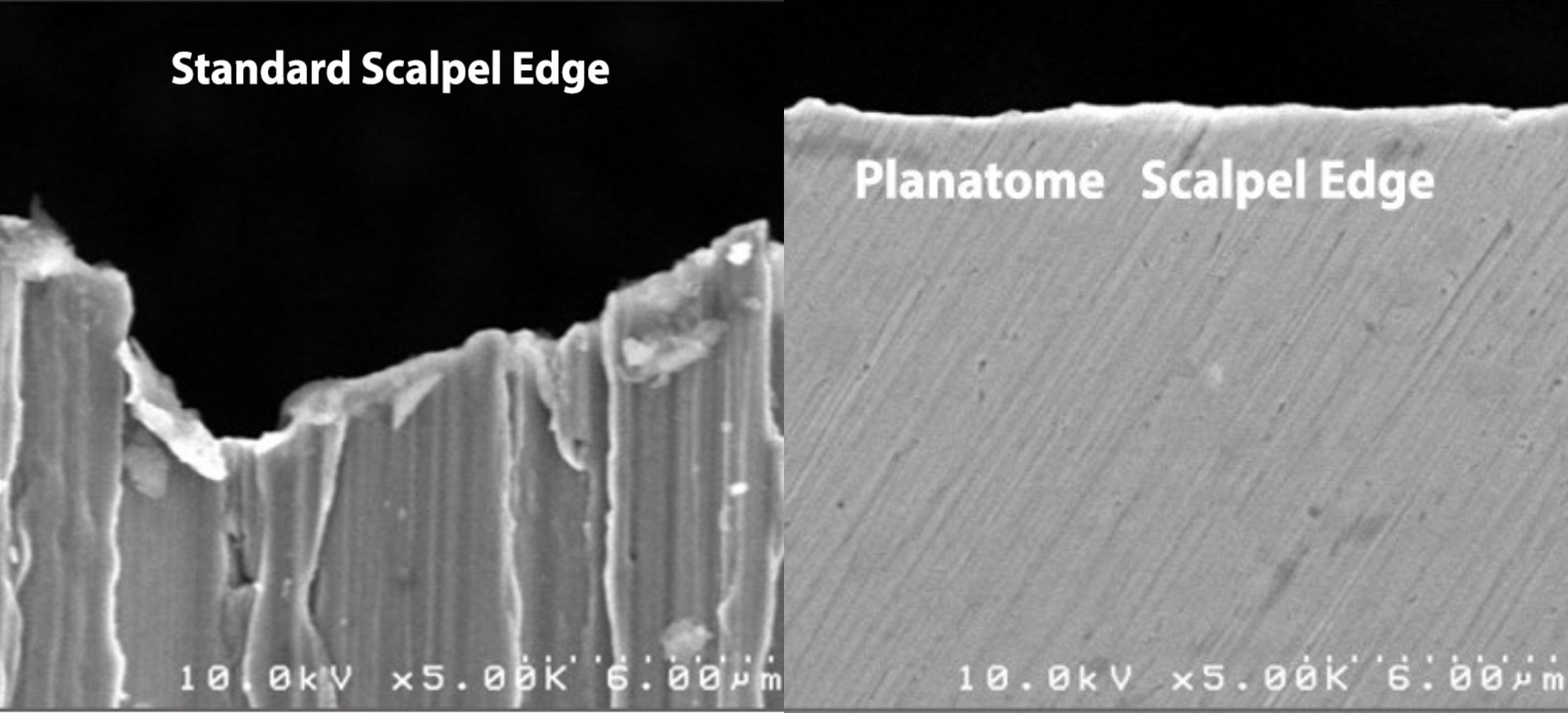
The American medtech start-up claims its Planatome technology – which applies a patented nano-polishing process to erase manufacturing defects found on standard scalpels – gives these surgical instruments an ultra-smooth, precise and consistent cutting surface.
This “dramatically minimises” trauma to human tissue during surgery, and improves post-procedure outcomes including faster healing, reduced chances of infections, increased wound strength, less scarring, less pain and reduced nerve damage – according to the company.
Entrepix Medical also says multiple studies have shown wound closure rates from incisions made using Planatome technology to be greater than 90% after 24 hours, compared to the 10% achieved with traditional scalpels.
Tim Tobin, CEO of Entrepix Medical, said: “Our atomically-smooth surgical blades are unlike all other scalpels on the market, with inherent benefits to the patient that are innately intuitive and can be life-changing.
“By employing a proven technology from the semiconductor industry, then adapting and perfecting it for use on surgical instruments, we provide surgeons an extraordinary version of their current preferred devices, dramatically transforming healing expectations through next-level performance.
“Research shows significant benefits when using a Planatome blade compared to a standard scalpel.”
New surgical blade technology from Entrepix Medical
Entrepix Medical states that, while the traditional scalpel blade has remained largely unchanged for close to 100 years now, its technology “transforms” these designs – by using nano-polishing to remove inconsistencies and defects, and make their surfaces molecularly-refined.
In addition to the study that indicated Planatome’s performance in improving wound closure rates, the company says data from another investigation shows that any nerves cut with a Planatome blade regenerate more efficiently, leading to less postoperative nerve damage.
Specifically, nerves incised with a Planatome blade demonstrated a 25% recovery five weeks after surgery, while a nerve cut with a standard scalpel showed a 9% recovery – and, after 12 weeks, the nerves incised with a Planatome blade showed a 92% recovery.
Another separate analysis showed a “rapid reduction” in pain markers when using a Planatome-treated blade, with macrophage density – an indicator for pain levels – being 160% higher in standard scalpels.
Entrepix Medical president and COO Bill Fender said: “Independent market research has shown that patients and surgeons alike are universally most concerned by the risks associated with postoperative complications.
“A Planatome blade is the only surgical instrument of its kind that provides the atomic level precision and consistency required to minimise these potential complications.
“With three additional patents pending, the benefits of Planatome technology will capture the scalpel and extend to a host of additional surgical instruments.”






